- Group websites
- Knauf Insulation worldwide
- Corporate
- Albania
- Algeria
- Australia
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bosnia
- Bulgaria
- Canada
- Croatia
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Italy
- Japan
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malaysia
- Mexico
- Montenegro
- Morocco
- Netherlands
- New Zealand
- Norway
- OEM
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- Serbia
- Singapore
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- South Korea
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Tunisia
- Turkey
- UAE
- USA
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- Knauf Insulation worldwide
- Group websites
- Knauf Insulation worldwide
- Corporate
- Albania
- Algeria
- Australia
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bosnia
- Bulgaria
- Canada
- Croatia
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Italy
- Japan
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malaysia
- Mexico
- Montenegro
- Morocco
- Netherlands
- New Zealand
- Norway
- OEM
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- Serbia
- Singapore
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- South Korea
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Tunisia
- Turkey
- UAE
- USA
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- Knauf Insulation worldwide
- Home
- Protect people and buildings with Fire-Safe Insulation
Protect people and buildings with Fire-Safe Insulation
KEY CONCEPTS AND REGULATIONS FOR EFFECTIVE FIRE SAFETY
Fire safety is a crucial consideration for any building or structure, and proper insulation plays a vital role in preventing fires from spreading and minimizing their impact. When it comes to insulation, it's essential to consider factors such as fire resistance, installation, and regulatory compliance. By understanding the critical role insulation plays in fire safety, we can take the necessary steps to protect our homes, buildings, and communities from the devastating effects of fires.
Fire safety and insulation are two important factors that should be considered together when it comes to protecting your home or building from fire. Here are some things you should know:
Insulation materials: The type of insulation material used can affect fire safety. Some insulation materials, such as fiberglass, mineral wool, and cellulose, are considered relatively safe in terms of fire hazards. However, even the best insulation materials can pose a fire risk if not installed properly.
Fire resistance rating: Insulation materials are rated based on their fire resistance. This rating measures how long a material can resist fire before it starts to burn. Higher fire resistance ratings indicate a material is less likely to ignite and spread fire.
Proper installation: Proper installation of insulation is essential for fire safety. Insulation should be installed with the proper clearance from heat sources, such as light fixtures or chimneys. It should also be installed without leaving gaps or voids that could allow flames to spread.

Why Insulation Plays a Crucial Role in Fire Safety?
Fire resistance in insulation can help protect people and property from the dangers of fire. In the event of a fire, fire-resistant insulation can slow the spread of flames and limit the amount of smoke and toxic gases released, giving people more time to escape and reducing the risk of injury or death.
Many building codes require that insulation meet certain fire-resistance standards in order to ensure that buildings are safe and comply with local regulations. Buildings that do not meet these standards may be deemed unsafe and may not be allowed to be occupied.
Fire-resistant insulation can also help reduce the risk of fire damage to buildings and property, which can lower insurance premiums for building owners and occupants. Fire-resistant insulation can also provide energy efficiency benefits by reducing heat loss and improving the overall energy performance of a building.
Know Your Fire Resistance Classes!
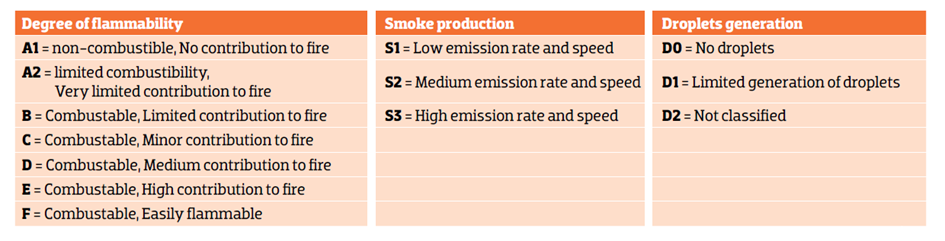
Reaction to fire indicates if the material supplies fuel to the fire before the flashover. This classification system is composed of seven groups ranking from A1 to F, where A1 is made up of non-combustible products and F of easily flammable products (Euroclass: A1 / A2 / B / C / D / E / F).
A1 – it does not fuel or contribute to the fire
A2 – little fuel and very low contribution to the fire, without causing flashover
B – little fuel and very low contribution to the fire, but they cause flashover
C – Fuel, causes flashover at ten minutes
D – Fuel, causes flashover before ten minutes
E – Fuel, causes flashover before two minutes
F – Indeterminate behaviour, materials and products untested
In addition to the seven classes, two supplementary criteria, S and D, are also taken into consideration:
S refers to smoke production, and products are classified as S1 or S3 based on the volume of smoke generated. S1 products generate minimal amounts of smoke that are slowly released and S3 generates a lot of smoke that is released fast.
D index indicates the likelihood of flaming droplets being generated, with D2 being the least desirable classification.
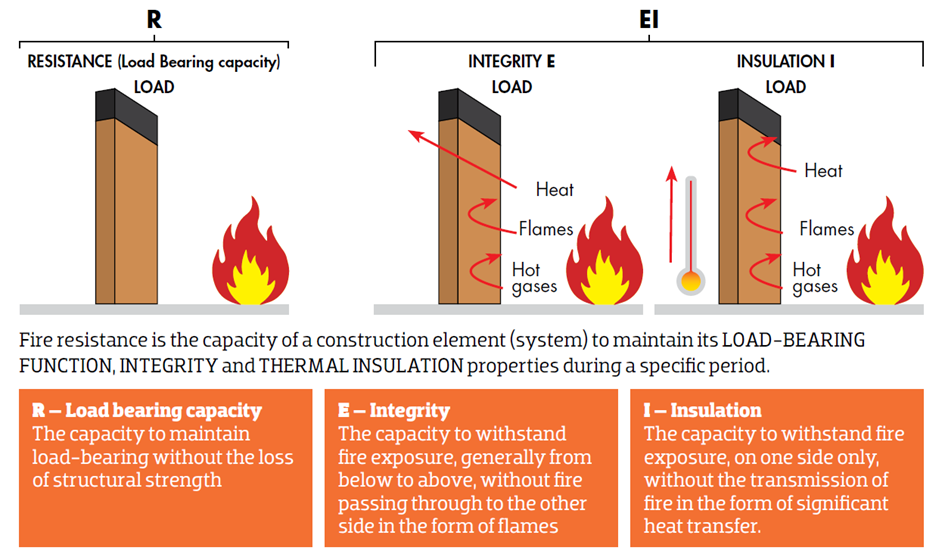
Fire resistance, on the other hand, is used to measure the amount of time a building component (such as a wall, door, or window) can withstand fire exposure before it fails. Fire ratings are usually expressed in minutes or hours, and they are determined through standardized fire tests.
The standard fire resistance rating values are 15, 30, 45, 60, 90, 120, 180 and 240 minutes, which typically means the period during which a passive fire protection system / construction element can withstand a standard fire resistance test. For example, a fire-rated wall may have a fire rating of 1 hour, meaning it can withstand fire exposure for 60 minutes before it fails. A fire-rated door may have a fire rating of 90 minutes, meaning it can withstand fire exposure for 90 minutes before it fails.
In order to classify the fire resistance of a building element, we need to assess this three performance characteristics: load-bearing capacity, integrity and insulation. Certain other optional characteristics can also be assessed, e.g. radiation, mechanical aspects, self-closing ability and smoke leakage.
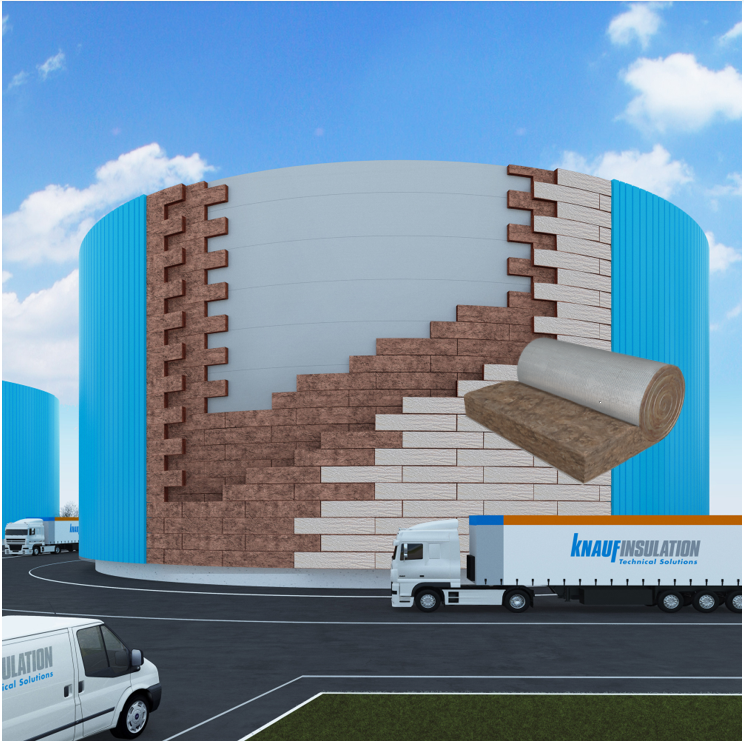
Passive structural fire protection is a crucial consideration in industries such as HVAC, shipbuilding, and process industry. It's essential to have highly effective fireproof insulation and appropriate fire containment measures to prevent the spread of flames, heat, and smoke in case of a fire. Our Fire-teK® mineral wool insulation products are specifically designed for this purpose and meet fire resistance classes EI30, EI60, EI90, and EI120. They not only provide excellent fire protection but also offer superior thermal and acoustic insulation properties. Knauf Insulation offers high-performance insulation with top-of-the-class fire resistance for technical installation.

Get in Line with Fire Safety Regulations
Fire safety regulations for insulation vary depending on the location and the type of building. However, here are some general guidelines and regulations that may apply:
Building codes
Building codes in most areas require that insulation materials meet certain fire safety standards. These codes typically specify the minimum fire resistance rating for insulation materials based on their location in the building.
Testing and certification
Insulation materials must be tested and certified to meet certain fire safety standards, such as ASTM E84, ASTM E119, UL 723, UL 1709, ISO 1182, U.S. Coast Guard 164.109, and others. The certification should be provided by a recognized third-party testing organization.
Clearance
Insulation materials should be installed with the proper clearance from heat sources, such as light fixtures or chimneys. Building codes usually specify the required clearance distance.
Fire barriers
Fire barriers, such as walls, ceilings, and floors, are required to be constructed with fire-resistant materials and be properly sealed to prevent flames from penetrating.
Sprinkler systems
In some cases, building codes may require the installation of fire sprinkler systems to control or extinguish fires in a building.
Fire safety plan
Building owners should have a fire safety plan in place that includes regular inspections and maintenance of insulation materials, as well as evacuation procedures and training for occupants.
It is important to check with your local building authority for specific fire safety regulations that apply to your location and building type. Following these regulations and guidelines can help ensure the safety of occupants and prevent the spread of fires in the building.
Find out more about fire protection and solutions we suggest in our Fire magazine.
Blog written by: Luka Klemen, DBP Brand Design Studio